Denaturation is a process in wich proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary, tertiary and secondary structure that is present in their native state. Denaturation is the result of the application of some external stress (heat and pH change) or compounds such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt or organic solvent.
OBJECTIVES:
1-Study the relation between the structure and the function of proteins.
2- Understand how temperature, pH and salinity affect to the protein structure.
CATALASE ACTIVITY:
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all-living organisms exposed to oxygen. It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen perioxide (H2O2) to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage and preventing the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide.
PROCEDURE:
In this experiment we are going to test the catalse activity in different environment situations. We are going to measure the rate of enzyme activity under various conditions, such as different pH values and temperatures. We will measure catalse activity by observing the oxygen gas bubbles when H2O2 is destroyed. If lots of bubbles are producted, it means the reaction is happening quickly and the catalase enzyme is very active.
1- Prepare 30 ml of H2O2 10% in a beaker (use a pipet)
2- Prepare 30 ml of HCL 10% in a beaker. -------> Solutions
3- Prepare 30 ml of NaCL 50% in a beaker.
4- Peel a fresh potato tuber and cut the tissue in five cubes of 1cm3. Weigh them and equal the mass.
5- Label 5 test tubes (1,2,3,4,5)
6- Immerse 10 minutes your piece of potato inside the HCL beaker
HCL SOLUTION
8- Boil another piece of potato.
9- With a mortar, mash up the third piece of potato.
10- Prepare 5 test tubes as indicated below:
11- Add 5ml H2O2 in each test tube
12- With a glass-marking pen mark the heigh of the bubbles. Measure it with a ruler.
13- Compare the results of the 5 test tubes.
Table with the important parts of the experiment:
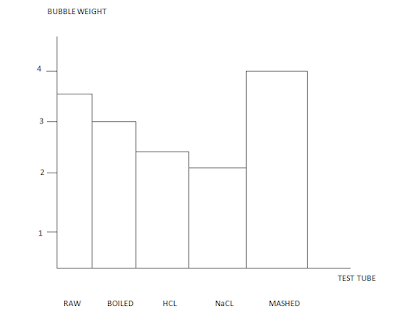
RESULTS:
QUESTIONS:
1. How did the temperature of the potato affect the activity of catalase?
Temperature denaturate the catalase.
2. How did the change of the pH of the potato affect the activity of catalase?
The change of the Ph denaturate the catalase.
3. In wich potato treatment was catalase the most active? Why do you think this was?
Mashed potato, because we had broken the cells and the catalase was more quickly.
4. An experiment was performed to test the effect of temperature and pH on the activity of Enzyme X. The following data was collected during the experiment:
a) What is the optimum pH of enzyme X? 8 (maximum activity)
b) What is the optimum temperature of enzyme X? 20 (maximum activity)
c) Why do you think enzyme X has low activity at a pH of 10? Because has been denatured
d) Enzyme X perfoms critical life functions. Use the data above to explain why a fever of 40 degrees may be dangerous.
Beacuse is more lower than the maximum activity.







No comments:
Post a Comment